app development
blockchain
+ 3 more ...
All You Need to Know About Blockchain
19 May 2020
by Lotte, Digital Content Specialist
19 May 2020
by Lotte, Digital Content Specialist
app development
blockchain
smart contracts
data protection
bitcoin
All You Need to Know About Blockchain
Table of contents
Contact us
We will get back to you in the next 48 hours.

Blockchain technology revolves around much more than just cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin.
Blockchain is a term we come across more and more often. Most of you probably know it best as the system used by the popular online cryptocurrency Bitcoin. But very few actually know how it works, and how blockchain is applicable to more than cryptocurrency. Because of blockchain’s decentralised nature and data integrity, it’s a system that’s increasingly often used in the development of mobile apps. This blog teaches you the basics of blockchain, and how blockchain is used by app developers.
Blockchain: the basics
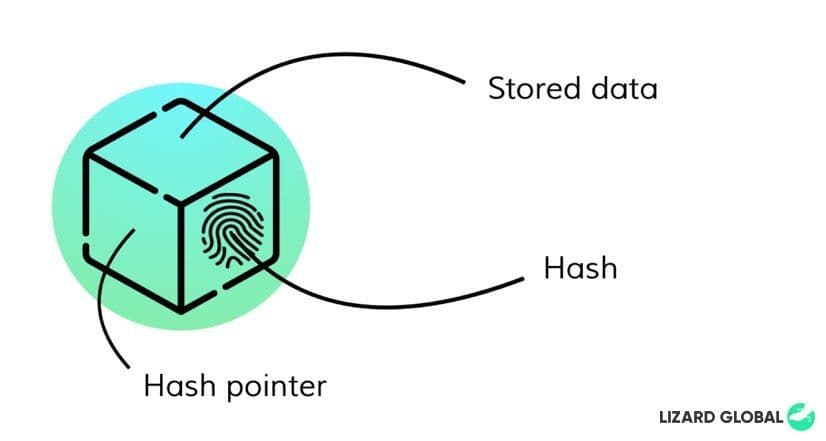
Blockchain is a decentralised and often open source technology which allows digital information to be distributed across the internet in an unregulated and integer way. Blockchain technology exists of an interconnectedness of unique blocks of data, which all possess their own identity, called “hashes”. These hashes are formulated by a unique combination of letters and numbers, never the same as another block, just like fingerprints.
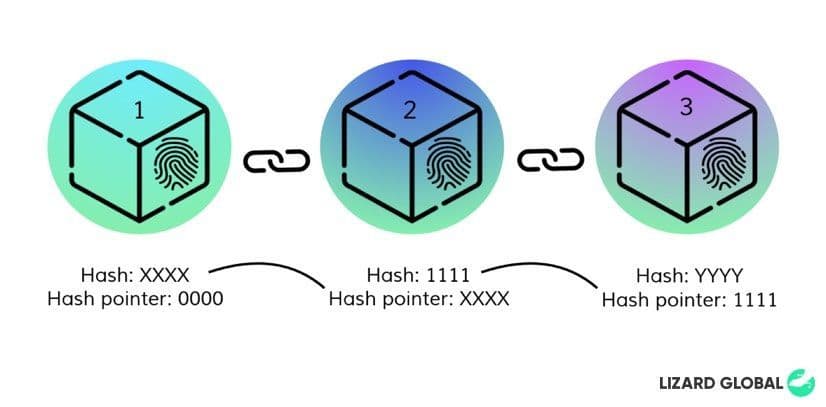
Individual blocks are connected to one another with a reference to its unique hash identity, a so-called “hash pointer”. For example, block 1 has the hash ID of “XXXX” and is connected to block 2, which contains a hash pointer “XXXX”, next to its own hash ID of “YYYY”. Block 3, with the ID of “ZZZZ”, contains the reference hash pointer (“YYYY”) of block 2. This way, all blocks are connected -or chained- in a specific order. Because one block is followed by another block connected by their code, it can not be replaced or misplaced. Blockchain technology possesses three core principles that make this type of data storage and distribution so unique and effective.
Decentralisation
Whereas centralised networks store all data in one central place, decentralised networks divide their data over different hubs with equal authority. Blockchain technology makes use of a so-called decentralised “peer-to-peer” (P2P) network, which means that everyone in the network fulfills the same role and has an equal level of authority. All users are downloaders as well as uploaders. Whereas centralised networks often consist of a “client-server” model, with a clear hierarchy of roles and overall authority: there is one central supplier opposed to a greater mass of receivers. This client-server architecture is generally much slower and sensitive to failure than distributed peer-to-peer networks.
A great disadvantage of centralised networks is its vulnerability to hacks and outages. If that one storage and transfer space is being meddled with, it affects all data. And if a centralised database shuts down for whatever reason, no one can access the information that is stored in that particular space. Because the data in decentralised networks is divided, potential hacks or breaches do not impact the entire database at once. And if one node shuts down, it doesn’t affect the rest of the network, which provides ongoing access to its users. Because of that, decentralised data transference has a greater sense of integrity than data stored in a centralised system.
Immutability
The immutability of blockchain means that, once a connection between data blocks is established, it’s close to impossible to meddle with. Because the individual blocks are connected by unique identifiers, it’s difficult to tamper with a single block without breaking the blockchain. Note that immutability does not imply that the data inside a blockchain is unchangeable. It's simply hard to meddle with without disrupting the system. The cryptographic signatures (or hash value) of a data block connect one data block to another, and therefore create a chain that’s difficult to intrude. The integrity of a blockchain greatly relies on their storage on nodes.
Nodes
To ensure the data integrity of blockchain, there are nodes, which form the infrastructure of blockchain and can basically be seen as copies of the same chain. Without nodes, a blockchain’s data would not be accessible from the outside. Data blocks are stored on nodes, which can be compared to small servers. All nodes are connected, and constantly exchange the latest blockchain data and transaction histories. When we’re talking about nodes of a blockchain, we’re speaking of millions of nodes, not just a couple. The system verifies the truth of the data stored in the chain by a 51% rule: If at least 51% of the node copies contain the same data, it’s true data. And because there are millions of nodes, it’s practically impossible to breach the system and change the truthfulness of the data. In that sense, the data in a blockchain is much more protected than in a system that is regulated by only a few servers.
Transparency
Probably one of the most interesting characteristics of blockchain technology is its quality to be simultaneously private, even anonymous, and transparent, for everyone to see and use. In our blog about cybersecurity, you can read more about cryptography and how Lizard Global deals with data privacy. As much as blockchain technology is private and secured, it’s also transparent. How is that possible, you ask? Although the stored data and identities are nearly impossible to meddle with, all data concerning copies of the history of transferrences and transactions are, in fact, viewable to everyone in the network.
The particular transparency that goes hand-in-hand with privacy is exactly what makes blockchain so unique and usable for cryptocurrency transactions. But not only cryptocurrency benefits from blockchain. So-called “smart contracts” also make use of blockchain technology. Smart contracts help its users to exchange and transfer money, shares, property, and anything with a certain value in a safely protected and efficient manner. Because blockchain technology is decentralised, it removes the need of a middleman or third party. All transactions happen directly between the sending party and the receiving party. Both Bitcoin and blockchains used for smart contracts can not exist without transparency, as it solves the problem of trust between parties who may not know each other. Because topics of trustability, incorruptibility and traceability are becoming increasingly important values in current society, blockchain is a very powerful technology with its focus on the future of data transfer.
Blockchain and DApps
Now we know the basics of blockchain, it’s time to take a look at why it’s such a beneficial technology for app development other than cryptocurrencies. A wide variety of industries, like e-commerce, healthcare, data management, e-governance and gaming are increasingly being supported by blockchain technology. A few commercial blockchains are open source and provide their users with a platform for developing so-called decentralised applications, or “DApps”. Two of the most popular blockchain networks are Bitcoin and Ethereum. And by now, quite a lot of apps that make use of blockchain technology are built on these existing open source P2P networks.
Some examples of brands that are developing their apps with blockchain technology in mind are Spotify, which uses a blockchain database for a decentralised connection between its tracks, artists, and licencing agreements. Or IBM Blockchain, which is a blockchain that helps companies in logistics and businesses with long supply chains with tracking the status of every product throughout the entire supply process, from production to distribution. It uses blockchain technology to keep track of all individual products and their current status in the process.
Blockchain technology at Lizard Global
At Lizard Global, we are skilled in using blockchain technology in our software development. Our experience with the implementation of solutions using smart contracts is continuously developing, growing along with all new technological innovations. An example of our experience with blockchain technology involves the development of a platform that, by making use of smart contracts, can help individuals build a trusted and decentralized credit history without the reliance on third party (centralized) credit monitoring services.
With the implementation of smart contracts we strive to achieve a trusted way for users to enter contracts and build a trusted credit history which will be:
- Safe
- Cost-effective
- Reliable
- Fast
Blockchain technology and smart contracts showcase how innovative technology can change the world around us. The possibilities are endless, and all industries can benefit from the implementation of smart contracts. They are already being used for financial trades and services, insurance, legal processes and agreements, but there is much more to discover. Healthcare, governments, business management: these are only some examples of industries that are greatly suitable for blockchain technology and smart contracts.
Want to know more about our experience with blockchain? Perhaps we can help you out with implementing blockchain technology in your app? Feel free to contact us, and we’ll see what we can do for you.

Blockchain technology revolves around much more than just cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin.
Blockchain is a term we come across more and more often. Most of you probably know it best as the system used by the popular online cryptocurrency Bitcoin. But very few actually know how it works, and how blockchain is applicable to more than cryptocurrency. Because of blockchain’s decentralised nature and data integrity, it’s a system that’s increasingly often used in the development of mobile apps. This blog teaches you the basics of blockchain, and how blockchain is used by app developers.
Blockchain: the basics
Blockchain is a decentralised and often open source technology which allows digital information to be distributed across the internet in an unregulated and integer way. Blockchain technology exists of an interconnectedness of unique blocks of data, which all possess their own identity, called “hashes”. These hashes are formulated by a unique combination of letters and numbers, never the same as another block, just like fingerprints.
Individual blocks are connected to one another with a reference to its unique hash identity, a so-called “hash pointer”. For example, block 1 has the hash ID of “XXXX” and is connected to block 2, which contains a hash pointer “XXXX”, next to its own hash ID of “YYYY”. Block 3, with the ID of “ZZZZ”, contains the reference hash pointer (“YYYY”) of block 2. This way, all blocks are connected -or chained- in a specific order. Because one block is followed by another block connected by their code, it can not be replaced or misplaced. Blockchain technology possesses three core principles that make this type of data storage and distribution so unique and effective.

Decentralisation
Whereas centralised networks store all data in one central place, decentralised networks divide their data over different hubs with equal authority. Blockchain technology makes use of a so-called decentralised “peer-to-peer” (P2P) network, which means that everyone in the network fulfills the same role and has an equal level of authority. All users are downloaders as well as uploaders. Whereas centralised networks often consist of a “client-server” model, with a clear hierarchy of roles and overall authority: there is one central supplier opposed to a greater mass of receivers. This client-server architecture is generally much slower and sensitive to failure than distributed peer-to-peer networks.
A great disadvantage of centralised networks is its vulnerability to hacks and outages. If that one storage and transfer space is being meddled with, it affects all data. And if a centralised database shuts down for whatever reason, no one can access the information that is stored in that particular space. Because the data in decentralised networks is divided, potential hacks or breaches do not impact the entire database at once. And if one node shuts down, it doesn’t affect the rest of the network, which provides ongoing access to its users. Because of that, decentralised data transference has a greater sense of integrity than data stored in a centralised system.
Immutability
The immutability of blockchain means that, once a connection between data blocks is established, it’s close to impossible to meddle with. Because the individual blocks are connected by unique identifiers, it’s difficult to tamper with a single block without breaking the blockchain. Note that immutability does not imply that the data inside a blockchain is unchangeable. It's simply hard to meddle with without disrupting the system. The cryptographic signatures (or hash value) of a data block connect one data block to another, and therefore create a chain that’s difficult to intrude. The integrity of a blockchain greatly relies on their storage on nodes.
Nodes
To ensure the data integrity of blockchain, there are nodes, which form the infrastructure of blockchain and can basically be seen as copies of the same chain. Without nodes, a blockchain’s data would not be accessible from the outside. Data blocks are stored on nodes, which can be compared to small servers. All nodes are connected, and constantly exchange the latest blockchain data and transaction histories. When we’re talking about nodes of a blockchain, we’re speaking of millions of nodes, not just a couple. The system verifies the truth of the data stored in the chain by a 51% rule: If at least 51% of the node copies contain the same data, it’s true data. And because there are millions of nodes, it’s practically impossible to breach the system and change the truthfulness of the data. In that sense, the data in a blockchain is much more protected than in a system that is regulated by only a few servers.

Transparency
Probably one of the most interesting characteristics of blockchain technology is its quality to be simultaneously private, even anonymous, and transparent, for everyone to see and use. In our blog about cybersecurity, you can read more about cryptography and how Lizard Global deals with data privacy. As much as blockchain technology is private and secured, it’s also transparent. How is that possible, you ask? Although the stored data and identities are nearly impossible to meddle with, all data concerning copies of the history of transferrences and transactions are, in fact, viewable to everyone in the network.
The particular transparency that goes hand-in-hand with privacy is exactly what makes blockchain so unique and usable for cryptocurrency transactions. But not only cryptocurrency benefits from blockchain. So-called “smart contracts” also make use of blockchain technology. Smart contracts help its users to exchange and transfer money, shares, property, and anything with a certain value in a safely protected and efficient manner. Because blockchain technology is decentralised, it removes the need of a middleman or third party. All transactions happen directly between the sending party and the receiving party. Both Bitcoin and blockchains used for smart contracts can not exist without transparency, as it solves the problem of trust between parties who may not know each other. Because topics of trustability, incorruptibility and traceability are becoming increasingly important values in current society, blockchain is a very powerful technology with its focus on the future of data transfer.
Blockchain and DApps
Now we know the basics of blockchain, it’s time to take a look at why it’s such a beneficial technology for app development other than cryptocurrencies. A wide variety of industries, like e-commerce, healthcare, data management, e-governance and gaming are increasingly being supported by blockchain technology. A few commercial blockchains are open source and provide their users with a platform for developing so-called decentralised applications, or “DApps”. Two of the most popular blockchain networks are Bitcoin and Ethereum. And by now, quite a lot of apps that make use of blockchain technology are built on these existing open source P2P networks.
Some examples of brands that are developing their apps with blockchain technology in mind are Spotify, which uses a blockchain database for a decentralised connection between its tracks, artists, and licencing agreements. Or IBM Blockchain, which is a blockchain that helps companies in logistics and businesses with long supply chains with tracking the status of every product throughout the entire supply process, from production to distribution. It uses blockchain technology to keep track of all individual products and their current status in the process.
Blockchain technology at Lizard Global
At Lizard Global, we are skilled in using blockchain technology in our software development. Our experience with the implementation of solutions using smart contracts is continuously developing, growing along with all new technological innovations. An example of our experience with blockchain technology involves the development of a platform that, by making use of smart contracts, can help individuals build a trusted and decentralized credit history without the reliance on third party (centralized) credit monitoring services.
With the implementation of smart contracts we strive to achieve a trusted way for users to enter contracts and build a trusted credit history which will be:
- Safe
- Cost-effective
- Reliable
- Fast
Blockchain technology and smart contracts showcase how innovative technology can change the world around us. The possibilities are endless, and all industries can benefit from the implementation of smart contracts. They are already being used for financial trades and services, insurance, legal processes and agreements, but there is much more to discover. Healthcare, governments, business management: these are only some examples of industries that are greatly suitable for blockchain technology and smart contracts.
Want to know more about our experience with blockchain? Perhaps we can help you out with implementing blockchain technology in your app? Feel free to contact us, and we’ll see what we can do for you.







