Design Thinking
Prototype
+ 3 more ...
How To Turn Problems Into Solutions With Design Thinking

14 Aug 2024
by Nadiy, Senior Content Writer

14 Aug 2024
by Nadiy, Senior Content Writer
Design Thinking
Prototype
Airbnb
Mobile App Development
Web App Development
How To Turn Problems Into Solutions With Design Thinking
Table of contents
Contact us
We will get back to you in the next 48 hours.

How To Turn Problems Into Solutions With Design Thinking Software Development
Discover how design thinking transforms challenges into opportunities by focusing on empathy, creativity, and iterative problem-solving. Learn the key stages of this innovative approach and how it can help you redefine problems, create user-centered solutions, and drive meaningful change in any industry. Unlock the power of design thinking today!
key takeaways
In an ever-changing world, businesses, individuals, and communities constantly face new challenges. Traditional problem-solving methods often fall short in addressing these dynamic issues, leaving a gap between the problem and the ideal solution. Enter design thinking—a human-centered approach that transforms problems into innovative solutions. This methodology has been embraced across industries, from technology and healthcare to education and public service.
But what exactly is design thinking, and how can it help turn problems into solutions?
Understanding Design Thinking
Design thinking is a solution-focused, problem-solving methodology that emphasizes understanding the user’s needs, redefining problems, and creating innovative solutions. Unlike traditional methods that might prioritize efficiency and feasibility, design thinking centers on empathy, creativity, and iteration.
This process involves several key stages:
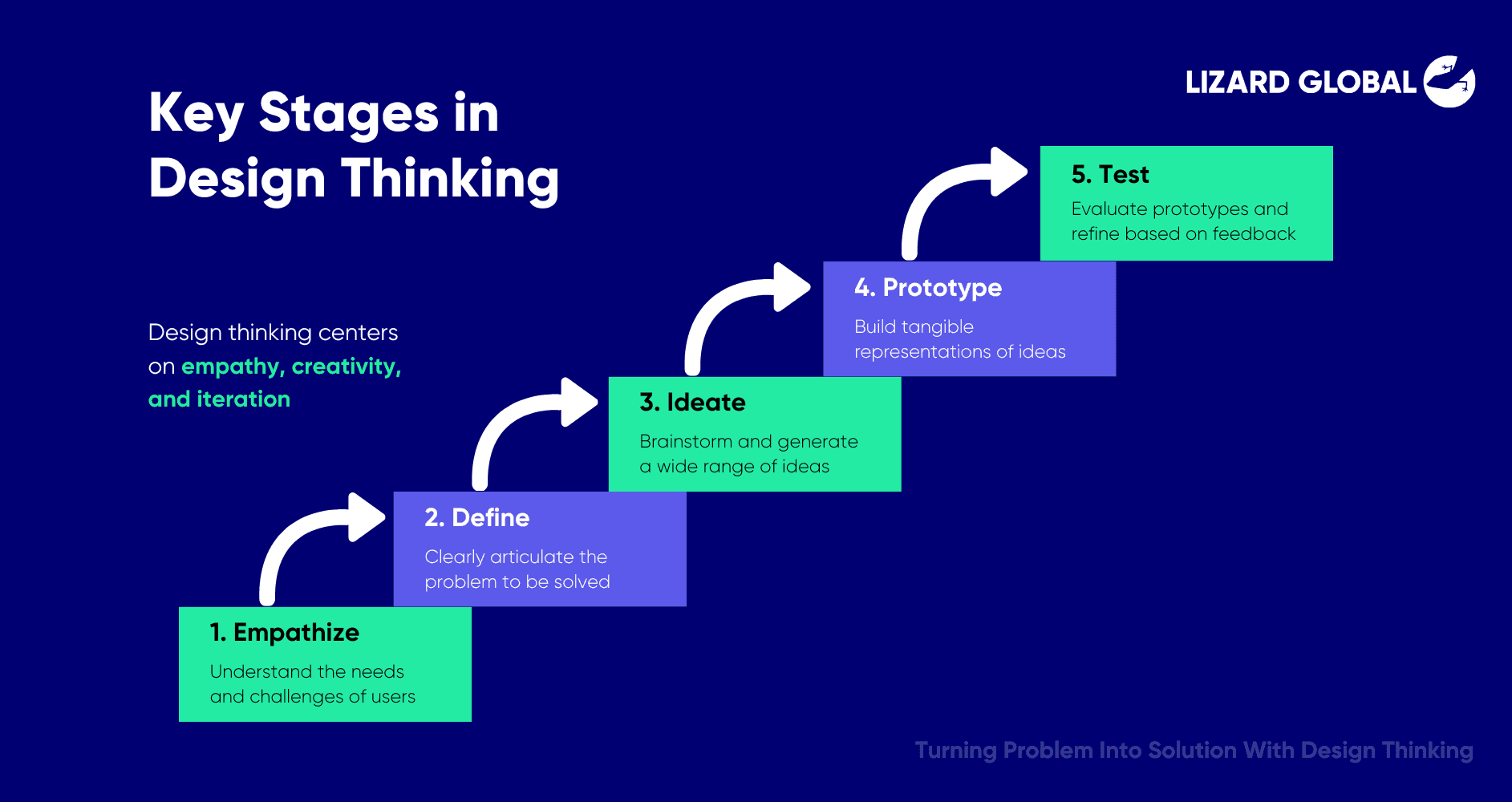
- Empathize: Understanding the needs and challenges of the users
- Define: Clearly articulating the problem to be solved
- Ideate: Brainstorming and generating a wide range of ideas
- Prototype: Building tangible representations of ideas
- Test: Evaluating the prototypes with real users and refining them based on feedback
The Power of Empathy: Understanding the Problem
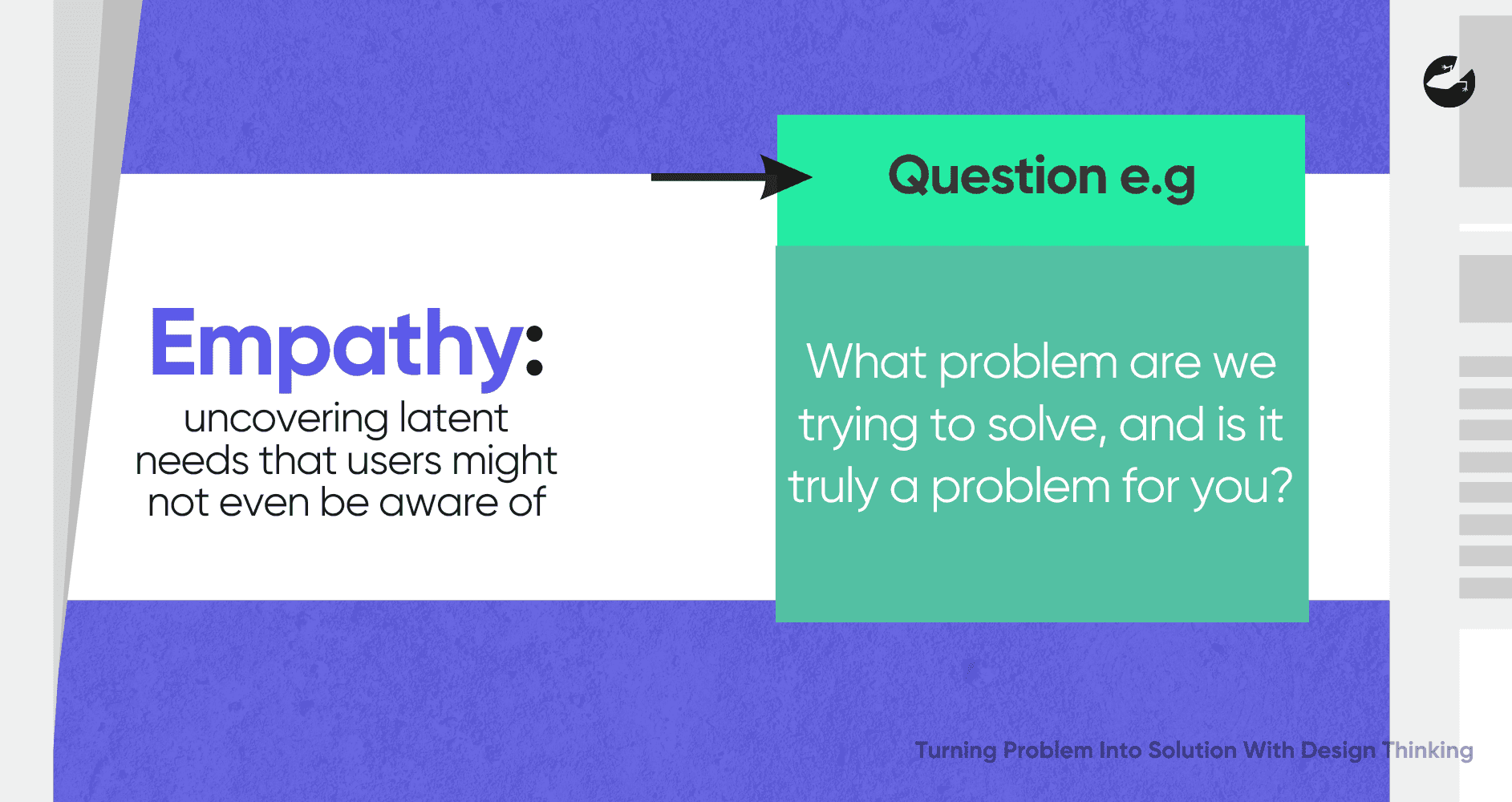
The first step in design thinking is to empathize with the user. This goes beyond simply identifying a problem; it requires deeply understanding the users, their environment, their behaviors, and their emotional states. Empathy helps in uncovering latent needs—those that users might not even be aware of. This can be done through the creation of a customer empathy map where the organizing and prioritizing of what the users want is laid out clearly.
For example, in the healthcare industry, understanding the emotional journey of a patient can lead to innovations that not only address their medical needs but also improve their overall experience. A design thinking approach might reveal that the anxiety patients feel while waiting for test results is a significant issue. This insight can lead to the development of a mobile app that provides timely updates and reassures patients during this stressful period.
Defining the Problem: Setting the Stage for Innovation
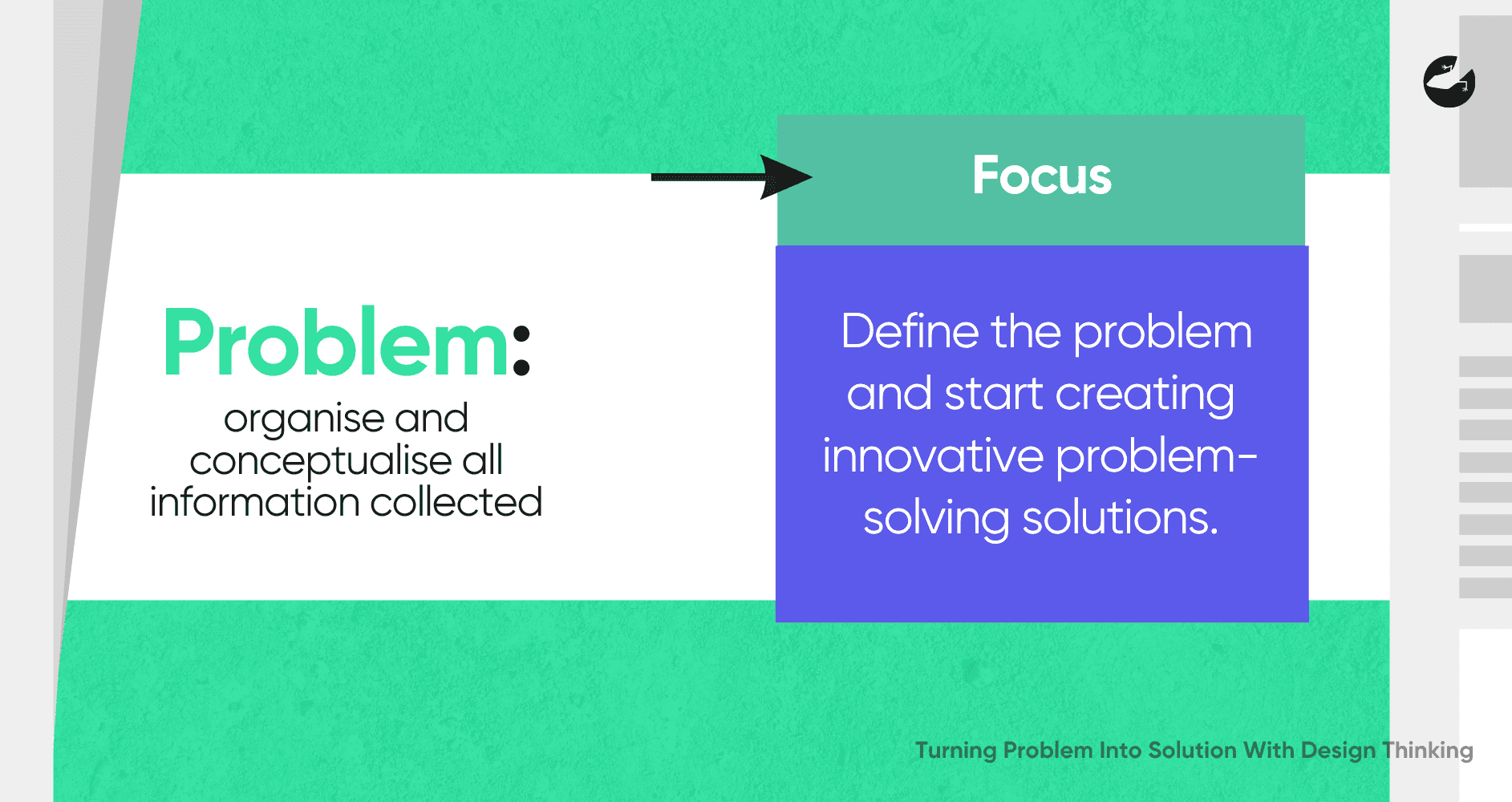
Once you have a deep understanding of the users, the next step is to define the problem clearly. This stage involves synthesizing the information gathered during the empathy phase to identify the core issues. The problem statement should be human-centered, focusing on the needs of the users rather than the organization.
For instance, instead of framing a problem as “We need to increase sales by 20%,” a design thinking approach would redefine it as “How might we create a shopping experience that delights our customers and encourages them to return?” This shift in perspective opens up new avenues for innovation, as the focus is now on improving the customer experience rather than merely boosting sales.
Do you know how Design Thinking and Agile Solutions go hand in hand? Read this blog to find out!
Ideation: Where Creativity Meets Feasibility
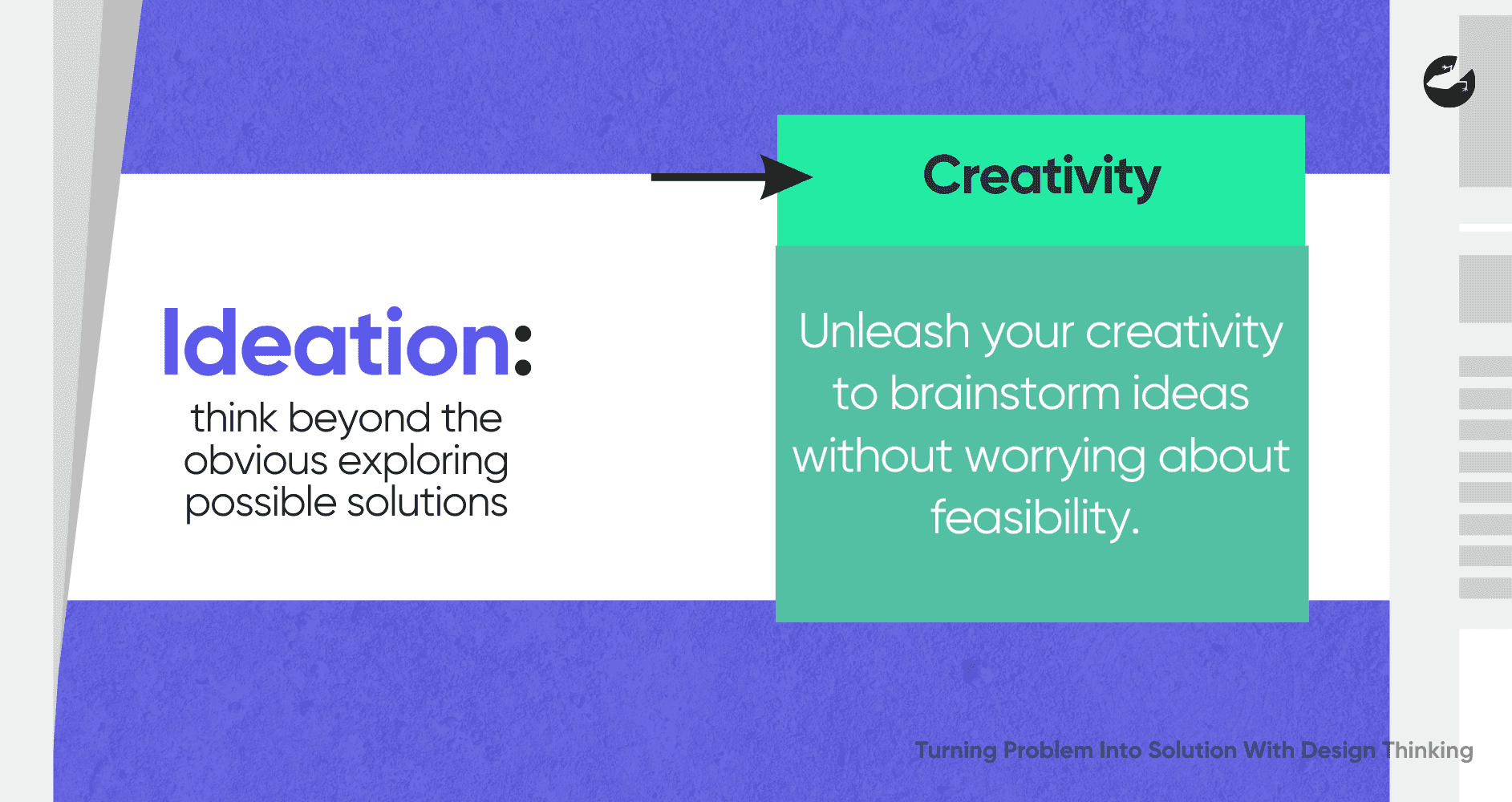
The ideation phase is where creativity is unleashed. This stage encourages thinking beyond the obvious and exploring a wide range of possible solutions. Brainstorming sessions, mind mapping, and sketching are common techniques used during this phase. The goal is to generate as many ideas as possible, without worrying about feasibility at this stage.
One of the key principles of design thinking is that no idea is too wild or too out-of-the-box. Often, the most unconventional ideas lead to the most innovative solutions. For example, in the automotive industry, the concept of self-driving cars seemed far-fetched a few decades ago. However, by pushing the boundaries of what was considered possible, companies like Tesla and Google have made autonomous vehicles a reality.
Prototyping: Bringing Ideas to Life
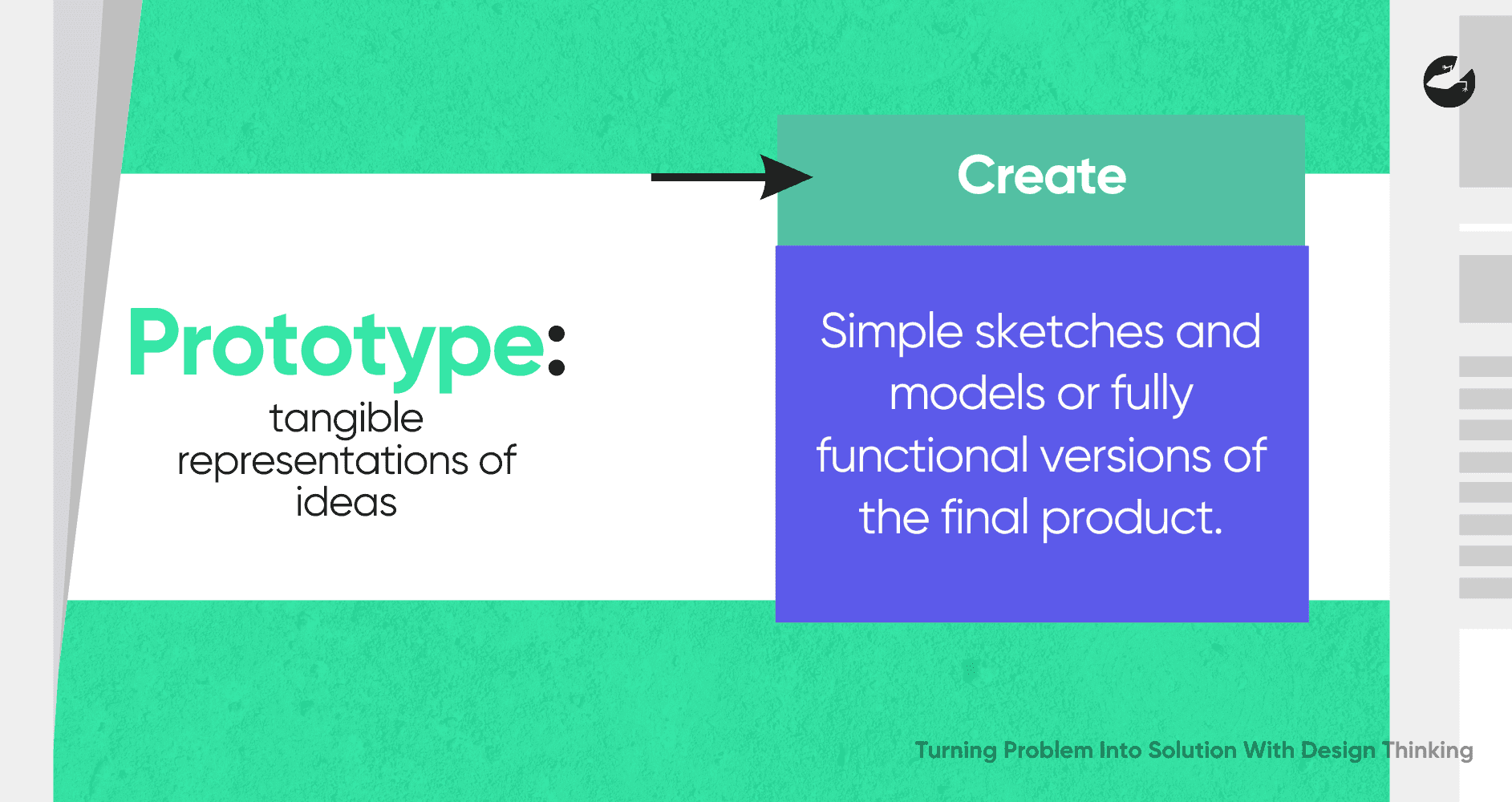
Prototyping
is where ideas take shape. This phase involves creating tangible representations of ideas, which can range from simple sketches and models to fully functional versions of the final product. Prototyping allows designers to explore how users interact with their solutions and identify potential flaws or areas for improvement.
In software development, for example, prototyping might involve creating a clickable mockup of an app. This allows designers and developers to test the user interface and user experience before committing to full-scale development. By identifying and addressing issues early in the process, teams can save time and resources, ultimately leading to a more polished final product.
Want to find out how much it costs to build your dream app or web app?
Testing: Iterating Towards Perfection

The final stage of design thinking is testing, where prototypes are evaluated by real users. This stage is crucial for gathering feedback and identifying areas where the solution can be refined. Testing is not a one-time event; it is an iterative process that involves multiple rounds of refinement until the solution fully meets the users’ needs.
For instance, in product design, testing might reveal that a certain feature is confusing to users or that the overall design doesn’t align with their expectations. Based on this feedback, the design team can go back to the drawing board, making necessary adjustments and improvements. This iterative approach ensures that the final product is not only functional but also user-friendly and effective in solving the problem.
Case Study: Airbnb – Redefining the Travel Experience

One of the most famous examples of design thinking in action is Airbnb. When the company was struggling to gain traction, the founders decided to apply design thinking principles to better understand the needs of their users. They traveled to New York to meet with hosts and guests, gaining insights into their experiences and challenges.
Through this empathetic approach, they discovered that poor-quality photos of listings were a significant pain point for users. In response, they rented a camera, took high-quality photos of the listings themselves, and saw an immediate increase in bookings. This small but impactful change was the result of deep empathy, a clear definition of the problem, and a willingness to iterate based on user feedback.
Today, Airbnb is a global success, largely due to its commitment to understanding and addressing the needs of its users. By applying design thinking, the company was able to turn a struggling startup into a multibillion-dollar business.
Why Design Thinking Matters?
Design thinking is more than just a methodology; it’s a mindset. It encourages organizations to look beyond traditional problem-solving approaches and to consider the human element in every solution. By focusing on the user, embracing creativity, and being willing to iterate, design thinking can lead to solutions that are not only innovative but also deeply resonant with those they are designed to serve.
Here’s why Design Thinking matters:
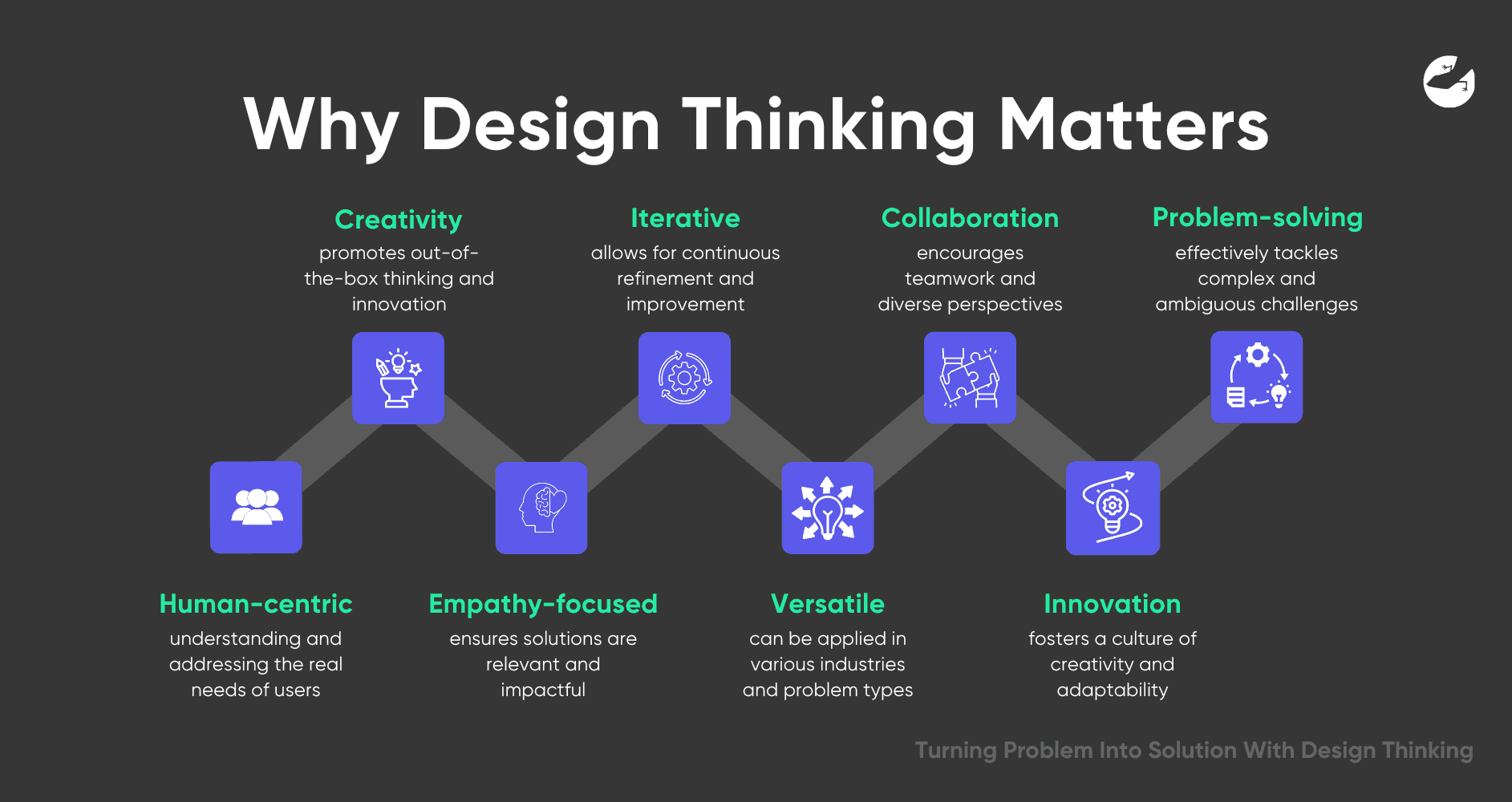
- Human-Centered Approach: Focuses on understanding and addressing the real needs of users.
- Encourages Creativity: Promotes out-of-the-box thinking and innovation.
- Emphasizes Empathy: Ensures solutions are relevant and impactful by deeply understanding users.
- Iterative Process: Allows for continuous refinement and improvement through prototyping and testing.
- Versatile Application: Can be applied across various industries and types of problems.
- Enhances Collaboration: Encourages teamwork and diverse perspectives in problem-solving.
- Drives Innovation: Helps organizations stay competitive by fostering a culture of creativity and adaptability.
- Solves Complex Problems: Effectively tackles complex and ambiguous challenges by redefining problems and exploring multiple solutions.
In today’s fast-paced world, the ability to adapt and innovate is more important than ever. Design thinking provides a framework for doing just that. Whether you’re designing a new product, improving a service, or addressing a complex social issue, design thinking can help you turn problems into solutions that are both effective and meaningful.
Embrace the Design Thinking Mindset With Lizard Global
The beauty of design thinking lies in its adaptability. It can be applied to virtually any problem, in any industry, and at any scale. From startups to Fortune 500 companies, organizations that embrace design thinking are better equipped to navigate the complexities of today’s world.

At Lizard Global when our clients are faced with a problem, we don’t just look for a solution with them—we think like a designer. We understand the people you’re designing for, redefine the problem in a human-centered way, and let our creativity flow. In doing so, we’ve not only solved many client problems but have also created truly valuable products that users love.
Join 2000+ subscribers
Stay in the loop with everything you need to know

How To Turn Problems Into Solutions With Design Thinking Software Development
Discover how design thinking transforms challenges into opportunities by focusing on empathy, creativity, and iterative problem-solving. Learn the key stages of this innovative approach and how it can help you redefine problems, create user-centered solutions, and drive meaningful change in any industry. Unlock the power of design thinking today!
In an ever-changing world, businesses, individuals, and communities constantly face new challenges. Traditional problem-solving methods often fall short in addressing these dynamic issues, leaving a gap between the problem and the ideal solution. Enter design thinking—a human-centered approach that transforms problems into innovative solutions. This methodology has been embraced across industries, from technology and healthcare to education and public service.
But what exactly is design thinking, and how can it help turn problems into solutions?
Understanding Design Thinking
Design thinking is a solution-focused, problem-solving methodology that emphasizes understanding the user’s needs, redefining problems, and creating innovative solutions. Unlike traditional methods that might prioritize efficiency and feasibility, design thinking centers on empathy, creativity, and iteration.
This process involves several key stages:

- Empathize: Understanding the needs and challenges of the users
- Define: Clearly articulating the problem to be solved
- Ideate: Brainstorming and generating a wide range of ideas
- Prototype: Building tangible representations of ideas
- Test: Evaluating the prototypes with real users and refining them based on feedback
The Power of Empathy: Understanding the Problem

The first step in design thinking is to empathize with the user. This goes beyond simply identifying a problem; it requires deeply understanding the users, their environment, their behaviors, and their emotional states. Empathy helps in uncovering latent needs—those that users might not even be aware of. This can be done through the creation of a customer empathy map where the organizing and prioritizing of what the users want is laid out clearly.
For example, in the healthcare industry, understanding the emotional journey of a patient can lead to innovations that not only address their medical needs but also improve their overall experience. A design thinking approach might reveal that the anxiety patients feel while waiting for test results is a significant issue. This insight can lead to the development of a mobile app that provides timely updates and reassures patients during this stressful period.
Defining the Problem: Setting the Stage for Innovation

Once you have a deep understanding of the users, the next step is to define the problem clearly. This stage involves synthesizing the information gathered during the empathy phase to identify the core issues. The problem statement should be human-centered, focusing on the needs of the users rather than the organization.
For instance, instead of framing a problem as “We need to increase sales by 20%,” a design thinking approach would redefine it as “How might we create a shopping experience that delights our customers and encourages them to return?” This shift in perspective opens up new avenues for innovation, as the focus is now on improving the customer experience rather than merely boosting sales.
Do you know how Design Thinking and Agile Solutions go hand in hand? Read this blog to find out!
Ideation: Where Creativity Meets Feasibility

The ideation phase is where creativity is unleashed. This stage encourages thinking beyond the obvious and exploring a wide range of possible solutions. Brainstorming sessions, mind mapping, and sketching are common techniques used during this phase. The goal is to generate as many ideas as possible, without worrying about feasibility at this stage.
One of the key principles of design thinking is that no idea is too wild or too out-of-the-box. Often, the most unconventional ideas lead to the most innovative solutions. For example, in the automotive industry, the concept of self-driving cars seemed far-fetched a few decades ago. However, by pushing the boundaries of what was considered possible, companies like Tesla and Google have made autonomous vehicles a reality.
Prototyping: Bringing Ideas to Life

Prototyping
is where ideas take shape. This phase involves creating tangible representations of ideas, which can range from simple sketches and models to fully functional versions of the final product. Prototyping allows designers to explore how users interact with their solutions and identify potential flaws or areas for improvement.
In software development, for example, prototyping might involve creating a clickable mockup of an app. This allows designers and developers to test the user interface and user experience before committing to full-scale development. By identifying and addressing issues early in the process, teams can save time and resources, ultimately leading to a more polished final product.
Want to find out how much it costs to build your dream app or web app?
Testing: Iterating Towards Perfection

The final stage of design thinking is testing, where prototypes are evaluated by real users. This stage is crucial for gathering feedback and identifying areas where the solution can be refined. Testing is not a one-time event; it is an iterative process that involves multiple rounds of refinement until the solution fully meets the users’ needs.
For instance, in product design, testing might reveal that a certain feature is confusing to users or that the overall design doesn’t align with their expectations. Based on this feedback, the design team can go back to the drawing board, making necessary adjustments and improvements. This iterative approach ensures that the final product is not only functional but also user-friendly and effective in solving the problem.
Case Study: Airbnb – Redefining the Travel Experience

One of the most famous examples of design thinking in action is Airbnb. When the company was struggling to gain traction, the founders decided to apply design thinking principles to better understand the needs of their users. They traveled to New York to meet with hosts and guests, gaining insights into their experiences and challenges.
Through this empathetic approach, they discovered that poor-quality photos of listings were a significant pain point for users. In response, they rented a camera, took high-quality photos of the listings themselves, and saw an immediate increase in bookings. This small but impactful change was the result of deep empathy, a clear definition of the problem, and a willingness to iterate based on user feedback.
Today, Airbnb is a global success, largely due to its commitment to understanding and addressing the needs of its users. By applying design thinking, the company was able to turn a struggling startup into a multibillion-dollar business.
Why Design Thinking Matters?
Design thinking is more than just a methodology; it’s a mindset. It encourages organizations to look beyond traditional problem-solving approaches and to consider the human element in every solution. By focusing on the user, embracing creativity, and being willing to iterate, design thinking can lead to solutions that are not only innovative but also deeply resonant with those they are designed to serve.
Here’s why Design Thinking matters:

- Human-Centered Approach: Focuses on understanding and addressing the real needs of users.
- Encourages Creativity: Promotes out-of-the-box thinking and innovation.
- Emphasizes Empathy: Ensures solutions are relevant and impactful by deeply understanding users.
- Iterative Process: Allows for continuous refinement and improvement through prototyping and testing.
- Versatile Application: Can be applied across various industries and types of problems.
- Enhances Collaboration: Encourages teamwork and diverse perspectives in problem-solving.
- Drives Innovation: Helps organizations stay competitive by fostering a culture of creativity and adaptability.
- Solves Complex Problems: Effectively tackles complex and ambiguous challenges by redefining problems and exploring multiple solutions.
In today’s fast-paced world, the ability to adapt and innovate is more important than ever. Design thinking provides a framework for doing just that. Whether you’re designing a new product, improving a service, or addressing a complex social issue, design thinking can help you turn problems into solutions that are both effective and meaningful.
Embrace the Design Thinking Mindset With Lizard Global
The beauty of design thinking lies in its adaptability. It can be applied to virtually any problem, in any industry, and at any scale. From startups to Fortune 500 companies, organizations that embrace design thinking are better equipped to navigate the complexities of today’s world.

At Lizard Global when our clients are faced with a problem, we don’t just look for a solution with them—we think like a designer. We understand the people you’re designing for, redefine the problem in a human-centered way, and let our creativity flow. In doing so, we’ve not only solved many client problems but have also created truly valuable products that users love.
Join 2000+ subscribers
Stay in the loop with everything you need to know
FAQs

How does Design Thinking help in solving problems?
Can Design Thinking be applied to any industry?
How do you start implementing Design Thinking in an organization?
What are some common challenges in using Design Thinking?
Is Design Thinking only for designers?
How does Design Thinking differ from traditional problem-solving methods?







