Software Development
Microservices
+ 3 more ...
How To Implement And Manage Microservices In An eCommerce Environment

13 May 2025
by Nadiy, Senior Content Writer

13 May 2025
by Nadiy, Senior Content Writer
Software Development
Microservices
eCommerce
Mobile App Development
Web App Development
How To Implement And Manage Microservices In An eCommerce Environment
Table of contents
Contact us
We will get back to you in the next 48 hours.

How To Implement And Manage Microservices In An eCommerce Environment
Struggling with scaling your eCommerce platform? Learn how microservices architecture can improve speed, resilience, and customer experience—plus a step-by-step guide tailored for eCommerce businesses.
key takeaways
The pressure to deliver seamless shopping experiences, handle traffic surges, and deploy new features rapidly has pushed eCommerce businesses to rethink their tech stack. Traditional monolithic systems simply can't keep up. That’s where microservices architecture steps in—offering the flexibility, scalability, and speed modern eCommerce platforms demand.
Whether you're launching a new online store or scaling an enterprise-level marketplace, microservices can transform how your system operates—but only when implemented and managed effectively.
What Are Microservices?
Before diving into the “hows” and “whys”, let’s first understand the “what”. Microservices are a software development architecture where applications are built as a suite of small, independent services. Each service performs a specific function (e.g., payment processing, user authentication, inventory management) and communicates with others via APIs.
This contrasts with a monolithic architecture, where all functions are interlinked and dependent on a single codebase. In an eCommerce setting, the shift from monolith to microservices enables faster development, better fault isolation, and easier scaling.
Benefits of Microservices for eCommerce
Now that we understand the “what” lets get into the “whys”. eCommerce platforms must deliver exceptional user experiences while handling complex, fast-changing requirements—from high traffic volumes and seasonal demand spikes to integrating third-party tools and launching frequent product updates. Microservices architecture directly addresses these challenges, making it a smart choice for modern digital commerce.
1. Unmatched Scalability
One of the most compelling reasons to adopt microservices in eCommerce is the ability to scale individual components independently. In a monolithic system, if the checkout process is experiencing high load, the entire application may need to scale—wasting server resources and driving up costs.
With microservices, you can scale just the checkout service without affecting other parts like search, user accounts, or reviews. This granular scaling ensures optimal performance and cost-efficiency, especially during traffic spikes like Black Friday or flash sales.
2. Accelerated Time-to-Market
In the world of eCommerce, being first to launch new features—like promo codes, loyalty programs, or one-click checkout—can give you a competitive edge. Microservices enable parallel development across teams, allowing multiple features to be built, tested, and deployed simultaneously.
This means faster innovation, reduced deployment risks, and the ability to continuously improve customer experiences without waiting for a full application release cycle.
3. Improved Fault Tolerance
System reliability is critical for online businesses—downtime equals lost revenue. In a monolithic application, one small bug can bring down the entire site. In contrast, microservices are designed with fault isolation in mind. If your recommendation engine crashes, it won’t affect order processing or payment gateways.
This modularity ensures that the system degrades gracefully and maintains core functionality even when certain services fail.
4. Greater Flexibility and Agility
Microservices give development teams the freedom to use different programming languages, frameworks, or databases for each service—choosing the best tool for the job.
For example, your search service could use Elasticsearch while your user authentication runs on Node.js.

This flexibility encourages innovation, shortens development time, and future-proofs your platform by avoiding vendor lock-in or outdated tech stacks.
5. Easier Third-Party Integrations
eCommerce platforms often rely on third-party services for payments (Stripe, PayPal), shipping (DHL, FedEx), analytics (Google Analytics), and more. With microservices, integrating these tools becomes easier and more secure.
You can build dedicated microservices for each third-party connection, maintaining cleaner codebases, faster testing, and better isolation in case an integration goes down.
6. Optimized DevOps and CI/CD Practices
Microservices work exceptionally well with DevOps pipelines and Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) practices. Each service can be independently tested, monitored, and updated without requiring full redeployment of the entire platform.
This creates a highly automated, low-risk deployment environment, ideal for agile eCommerce teams aiming to move quickly and stay ahead of market trends.
7. Localized Performance Enhancements
With microservices, you can optimize specific services based on user behavior or market needs. For example, you might optimize the product catalog for mobile responsiveness in one region while boosting load times for checkout services in another.
This localized tuning is difficult to achieve in tightly coupled monolithic systems and provides a performance edge in global markets.
Key Considerations Before Implementation
Before diving into microservices, it’s crucial to lay a strong foundation. Implementing microservices in an eCommerce environment isn’t just about choosing the right tech—it’s about understanding your business needs, architecture goals, and long-term strategy.
Taking the time to evaluate these key considerations will help you avoid common pitfalls and set your implementation up for long-term success:
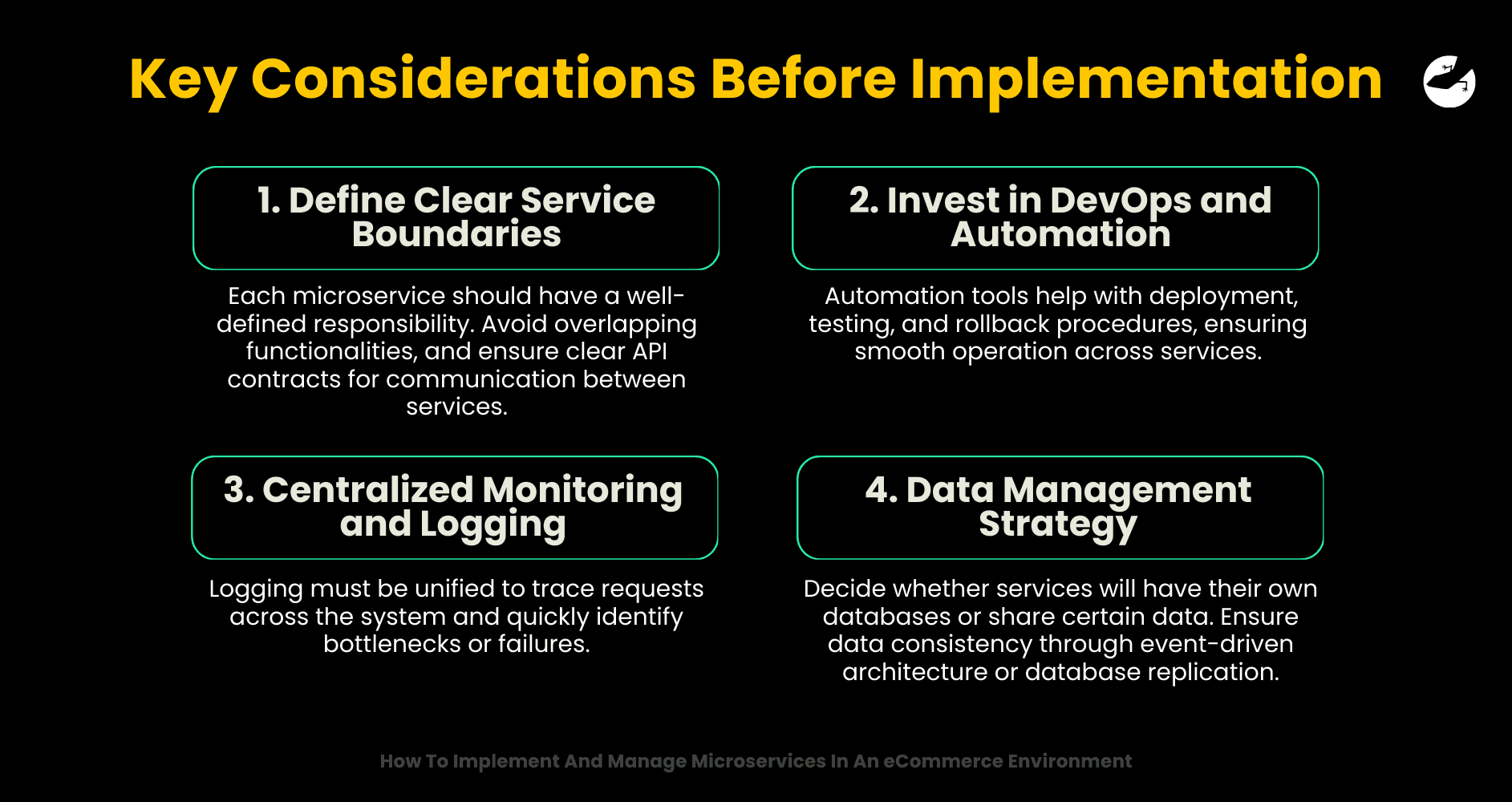
1. Define Clear Service Boundaries
Each microservice should have a well-defined responsibility. Avoid overlapping functionalities, and ensure clear API contracts for communication between services.
2. Invest in DevOps and Automation
Continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines are essential for managing microservices at scale. Automation tools help with deployment, testing, and rollback procedures, ensuring smooth operation across services.
3. Centralized Monitoring and Logging
Visibility is key. Implement tools like Prometheus, Grafana, or ELK Stack to monitor the health of individual services. Logging must be unified to trace requests across the system and quickly identify bottlenecks or failures.
4. Data Management Strategy
Microservices often require decentralized data management, which introduces complexity. Decide whether services will have their own databases or share certain data. Ensure data consistency through event-driven architecture or database replication.
Want to find out how much it costs to build your dream app or web app?
Step-by-Step Guide to Implementing Microservices in eCommerce
Transitioning to a microservices architecture is a strategic shift—not just a technical one. It requires careful planning, incremental rollout, and strong collaboration across development, DevOps, and business teams. Below is a comprehensive, step-by-step roadmap tailored to eCommerce platforms.
Step 1: Conduct a System Audit and Identify Service Domains
Before you write a single line of microservices code, assess your current system. The goal is to map out your platform's existing functionality and identify potential microservices.
Key Actions:
- Break down your monolith into logical business domains (e.g., product catalog, shopping cart, user authentication, payment processing)
- Document data flows and API dependencies
- Identify pain points like bottlenecks, scalability issues, or tightly coupled features
Pro Tip: Use Domain-Driven Design (DDD) to define clear service boundaries.
Step 2: Choose a Microservice to Start With
Don't try to rebuild your entire eCommerce system at once. Start with a low-risk, high-value feature that can be easily decoupled—like the recommendation engine or product search.
Key Actions:
- Prioritize a non-critical but functional service
- Ensure it has minimal dependencies on the rest of the system
- Set up a clear API for communication between the microservice and your existing platform
Pro Tip: Treat this initial service as your MVP to validate microservices in your environment.
Step 3: Define the Right Tech Stack for Each Service
One of the biggest advantages of microservices is tech stack flexibility. However, this can also create fragmentation if not managed carefully.
Key Actions:
- Evaluate technologies best suited for each microservice (e.g., Node.js for real-time, Python for data-heavy logic)
- Choose appropriate databases—some services might need SQL, others NoSQL
- Establish company-wide guidelines for coding standards, testing, and documentation
Pro Tip: Don't go overboard with variety—use flexibility where it counts, but keep things maintainable.
Step 4: Containerize Microservices with Docker
Packaging each microservice into a container ensures it’s portable, scalable, and isolated from other services.
Key Actions:
- Build Docker images for each microservice.
- Ensure all dependencies are packaged within the container
- Test locally and in staging environments for consistent behavior
Pro Tip: Use multi-stage builds to keep Docker images lightweight and secure.
Step 5: Orchestrate with Kubernetes or Similar Tools
As your number of microservices grows, manual deployment becomes infeasible. That’s where orchestration tools like Kubernetes step in.
Key Actions:
- Deploy containers using Kubernetes (or alternatives like AWS ECS, Docker Swarm)
- Set up service discovery and load balancing between containers
- Use Helm charts for repeatable deployments
Pro Tip: Leverage Kubernetes’ auto-scaling capabilities to handle eCommerce traffic spikes.
Step 6: Implement API Gateway and Service Communication
Microservices need to talk to each other securely and efficiently. An API Gateway serves as the single entry point to manage these interactions.
Key Actions:
- Use API gateways like Kong, AWS API Gateway, or NGINX
- Handle routing, rate limiting, authentication, and request transformation through the gateway
- Choose appropriate protocols (REST, gRPC) and message brokers (Kafka, RabbitMQ) for service-to-service communication
Pro Tip: Keep internal and external APIs separate to improve security and control.
Step 7: Set Up Centralized Monitoring and Logging
With many services running independently, observability becomes critical for performance and debugging.
Key Actions:
- Integrate monitoring tools like Prometheus, Grafana, and New Relic
- Set up logging with the ELK Stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana) or Fluentd
- Track metrics like uptime, response times, and error rates for each microservice
Pro Tip: Use correlation IDs to trace a user request across multiple services.
Step 8: Automate with CI/CD Pipelines
To support the rapid development and deployment of microservices, automation is essential.
Key Actions:
- Build CI/CD pipelines using Jenkins, GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, or Bitbucket Pipelines
- Automate testing (unit, integration, contract) and deployments to staging/production
- Enable automated rollbacks in case of failure
Pro Tip: Use feature flags for safe rollouts and A/B testing.
Step 9: Implement Robust Security Measures
Security must be embedded from the beginning—not bolted on afterward.
Key Actions:
- Secure APIs using OAuth 2.0, JWTs, and HTTPS
- Isolate services using network policies and firewalls
- Regularly scan containers and code for vulnerabilities
Pro Tip: Make security part of your CI/CD pipeline using automated tools like Snyk or Aqua Security.
Step 10: Continuously Iterate and Optimize
Microservices are not a one-and-done project. They require ongoing iteration, refactoring, and performance tuning.
Key Actions:
- Schedule regular code reviews and architectural assessments
- Decommission or refactor underperforming services
- Gather user feedback to guide enhancements
Pro Tip: Implement a service registry (like Consul or Eureka) for dynamic service discovery and lifecycle management.
By following these steps, you can transition from a tightly coupled monolith to a flexible, scalable, and high-performing microservices architecture that grows with your eCommerce business. The key is to start small, automate early, monitor deeply, and iterate continuously.
Managing Microservices Over Time
Successfully implementing microservices is just the beginning—the real challenge lies in managing them effectively over the long term. As your microservice ecosystem grows, maintaining stability, performance, and agility requires ongoing effort, solid governance, and the right tooling.
Here's how to stay in control and continue delivering value without letting complexity spiral out of control:
1. Service Lifecycle Management
Each microservice has its own lifecycle—from development and deployment to maintenance, versioning, and eventual deprecation. Without a plan, you risk accumulating “service sprawl.”
Best Practices:
- Document ownership: Assign clear ownership for each service to specific teams
- Version control: Use semantic versioning to manage backward compatibility and rolling upgrades
- Retirement protocols: Regularly audit services and decommission those that are outdated or unused
Tip: Keep a service catalog or registry (e.g., Backstage, Consul) to track status, endpoints, and ownership.
2. Monitoring, Logging & Observability
In a distributed system, traditional monitoring falls short. You need comprehensive observability to identify bottlenecks, debug errors, and understand system behavior in real time.
Key Tools:
- Monitoring: Prometheus, Grafana, Datadog, New Relic
- Logging: ELK Stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana), Fluentd
- Tracing: OpenTelemetry, Jaeger, Zipkin
Best Practices:
- Collect logs, metrics, and traces from every service
- Implement centralized dashboards for visibility
- Set automated alerts for latency, errors, and resource limits
Tip: Use correlation IDs to trace user sessions across multiple microservices.
3. Security Maintenance
With more entry points and data flows, security becomes more complex in a microservices environment. Ongoing management is critical to prevent vulnerabilities from slipping through the cracks.
Key Actions:
- Enforce mutual TLS for service-to-service communication
- Use OAuth 2.0 or JWT for authentication
- Regularly scan containers and dependencies for vulnerabilities with tools like Snyk or Aqua
- Apply least privilege access control via role-based access (RBAC) and network policies
Tip: Automate security updates in your CI/CD pipelines to reduce manual patching.
4. Configuration & Secrets Management
Each microservice has its own configuration—often per environment. Poor configuration handling can lead to instability and data breaches.
Best Practices:
- Use centralized configuration tools like Spring Cloud Config or HashiCorp Consul
- Store sensitive data (API keys, DB passwords) in secret management tools like Vault, AWS Secrets Manager, or Kubernetes Secrets
- Automate configuration changes through GitOps workflows
Tip: Avoid hardcoding configs or secrets—this is a common and dangerous anti-pattern.
5. Automated Deployments and Rollbacks
As the number of microservices increases, manual deployment becomes a bottleneck. You need reliable, repeatable deployment practices across services.
Best Practices:
- Use CI/CD tools (e.g., GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, Jenkins) to automate builds, tests, and deployments
- Integrate canary or blue/green deployments for safe rollouts
- Implement automated rollback strategies triggered by error thresholds or failed health checks
Tip: Use feature flags to release new functionality gradually and safely.
6. Testing Across Services
Testing in microservices requires more than just unit tests. You need to ensure that individual services and their interactions work as expected.
Testing Strategies:
- Unit testing for isolated service logic
- Contract testing to verify API agreements (e.g., Pact)
- Integration testing across service boundaries
- End-to-end testing for real-world scenarios
Tip: Automate tests within your CI/CD pipeline to catch issues early.
7. Service Coordination and Communication
As more services come online, managing how they talk to each other becomes critical for performance and reliability.
Best Practices:
- Avoid tight coupling—use event-driven architectures where possible
- Use asynchronous messaging with Kafka, RabbitMQ, or AWS SQS to reduce latency and failures
- Implement circuit breakers and retry logic to handle network issues gracefully
Tip: A service mesh like Istio can provide observability, security, and traffic control for inter-service communication.
8. Team Structure & Organizational Alignment
Managing microservices at scale requires alignment across people, process, and technology.
Organizational Tips:
- Use the “you build it, you run it” approach—developers maintain ownership post-deployment
- Structure teams around business capabilities, not technical layers
- Promote cross-functional collaboration between developers, DevOps, QA, and security
Tip: Consider adopting a DevOps or SRE model to sustain long-term microservices reliability.
Managing microservices over time is about staying proactive, not reactive. With the right architecture, automation, monitoring, and team culture, you can keep your eCommerce platform robust, agile, and customer-ready—no matter how complex it gets.
How Lizard Global Helps You Succeed with Microservices
At Lizard Global, we specialize in architecting and scaling powerful eCommerce platforms using modern microservices infrastructure. Whether you're transitioning from a legacy monolith or launching a high-performance platform from scratch, we help you:
- Design and implement microservices with optimal service boundaries
- Integrate CI/CD pipelines for seamless development and deployment
- Build resilient systems with smart monitoring and alerting tools
- Secure your services with best-in-class practices and API management
- Scale your infrastructure using Kubernetes and cloud-native tools
Our team of experts ensures your digital commerce business is fast, flexible, and future-ready, empowering you to stay ahead in a competitive marketplace.
Ready to revolutionize your eCommerce architecture with microservices? Let’s connect and make it happen.
Join 2000+ subscribers
Stay in the loop with everything you need to know

How To Implement And Manage Microservices In An eCommerce Environment
Struggling with scaling your eCommerce platform? Learn how microservices architecture can improve speed, resilience, and customer experience—plus a step-by-step guide tailored for eCommerce businesses.
The pressure to deliver seamless shopping experiences, handle traffic surges, and deploy new features rapidly has pushed eCommerce businesses to rethink their tech stack. Traditional monolithic systems simply can't keep up. That’s where microservices architecture steps in—offering the flexibility, scalability, and speed modern eCommerce platforms demand.
Whether you're launching a new online store or scaling an enterprise-level marketplace, microservices can transform how your system operates—but only when implemented and managed effectively.
What Are Microservices?
Before diving into the “hows” and “whys”, let’s first understand the “what”. Microservices are a software development architecture where applications are built as a suite of small, independent services. Each service performs a specific function (e.g., payment processing, user authentication, inventory management) and communicates with others via APIs.

This contrasts with a monolithic architecture, where all functions are interlinked and dependent on a single codebase. In an eCommerce setting, the shift from monolith to microservices enables faster development, better fault isolation, and easier scaling.
Benefits of Microservices for eCommerce
Now that we understand the “what” lets get into the “whys”. eCommerce platforms must deliver exceptional user experiences while handling complex, fast-changing requirements—from high traffic volumes and seasonal demand spikes to integrating third-party tools and launching frequent product updates. Microservices architecture directly addresses these challenges, making it a smart choice for modern digital commerce.
1. Unmatched Scalability
One of the most compelling reasons to adopt microservices in eCommerce is the ability to scale individual components independently. In a monolithic system, if the checkout process is experiencing high load, the entire application may need to scale—wasting server resources and driving up costs.

With microservices, you can scale just the checkout service without affecting other parts like search, user accounts, or reviews. This granular scaling ensures optimal performance and cost-efficiency, especially during traffic spikes like Black Friday or flash sales.
2. Accelerated Time-to-Market
In the world of eCommerce, being first to launch new features—like promo codes, loyalty programs, or one-click checkout—can give you a competitive edge. Microservices enable parallel development across teams, allowing multiple features to be built, tested, and deployed simultaneously.

This means faster innovation, reduced deployment risks, and the ability to continuously improve customer experiences without waiting for a full application release cycle.
3. Improved Fault Tolerance
System reliability is critical for online businesses—downtime equals lost revenue. In a monolithic application, one small bug can bring down the entire site. In contrast, microservices are designed with fault isolation in mind. If your recommendation engine crashes, it won’t affect order processing or payment gateways.

This modularity ensures that the system degrades gracefully and maintains core functionality even when certain services fail.
4. Greater Flexibility and Agility
Microservices give development teams the freedom to use different programming languages, frameworks, or databases for each service—choosing the best tool for the job.
For example, your search service could use Elasticsearch while your user authentication runs on Node.js.

This flexibility encourages innovation, shortens development time, and future-proofs your platform by avoiding vendor lock-in or outdated tech stacks.
5. Easier Third-Party Integrations
eCommerce platforms often rely on third-party services for payments (Stripe, PayPal), shipping (DHL, FedEx), analytics (Google Analytics), and more. With microservices, integrating these tools becomes easier and more secure.

You can build dedicated microservices for each third-party connection, maintaining cleaner codebases, faster testing, and better isolation in case an integration goes down.
6. Optimized DevOps and CI/CD Practices
Microservices work exceptionally well with DevOps pipelines and Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) practices. Each service can be independently tested, monitored, and updated without requiring full redeployment of the entire platform.

This creates a highly automated, low-risk deployment environment, ideal for agile eCommerce teams aiming to move quickly and stay ahead of market trends.
7. Localized Performance Enhancements
With microservices, you can optimize specific services based on user behavior or market needs. For example, you might optimize the product catalog for mobile responsiveness in one region while boosting load times for checkout services in another.

This localized tuning is difficult to achieve in tightly coupled monolithic systems and provides a performance edge in global markets.
Key Considerations Before Implementation
Before diving into microservices, it’s crucial to lay a strong foundation. Implementing microservices in an eCommerce environment isn’t just about choosing the right tech—it’s about understanding your business needs, architecture goals, and long-term strategy.
Taking the time to evaluate these key considerations will help you avoid common pitfalls and set your implementation up for long-term success:

1. Define Clear Service Boundaries
Each microservice should have a well-defined responsibility. Avoid overlapping functionalities, and ensure clear API contracts for communication between services.
2. Invest in DevOps and Automation
Continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines are essential for managing microservices at scale. Automation tools help with deployment, testing, and rollback procedures, ensuring smooth operation across services.
3. Centralized Monitoring and Logging
Visibility is key. Implement tools like Prometheus, Grafana, or ELK Stack to monitor the health of individual services. Logging must be unified to trace requests across the system and quickly identify bottlenecks or failures.
4. Data Management Strategy
Microservices often require decentralized data management, which introduces complexity. Decide whether services will have their own databases or share certain data. Ensure data consistency through event-driven architecture or database replication.
Want to find out how much it costs to build your dream app or web app?
Step-by-Step Guide to Implementing Microservices in eCommerce
Transitioning to a microservices architecture is a strategic shift—not just a technical one. It requires careful planning, incremental rollout, and strong collaboration across development, DevOps, and business teams. Below is a comprehensive, step-by-step roadmap tailored to eCommerce platforms.
Step 1: Conduct a System Audit and Identify Service Domains
Before you write a single line of microservices code, assess your current system. The goal is to map out your platform's existing functionality and identify potential microservices.

Key Actions:
- Break down your monolith into logical business domains (e.g., product catalog, shopping cart, user authentication, payment processing)
- Document data flows and API dependencies
- Identify pain points like bottlenecks, scalability issues, or tightly coupled features
Pro Tip: Use Domain-Driven Design (DDD) to define clear service boundaries.
Step 2: Choose a Microservice to Start With
Don't try to rebuild your entire eCommerce system at once. Start with a low-risk, high-value feature that can be easily decoupled—like the recommendation engine or product search.

Key Actions:
- Prioritize a non-critical but functional service
- Ensure it has minimal dependencies on the rest of the system
- Set up a clear API for communication between the microservice and your existing platform
Pro Tip: Treat this initial service as your MVP to validate microservices in your environment.
Step 3: Define the Right Tech Stack for Each Service
One of the biggest advantages of microservices is tech stack flexibility. However, this can also create fragmentation if not managed carefully.

Key Actions:
- Evaluate technologies best suited for each microservice (e.g., Node.js for real-time, Python for data-heavy logic)
- Choose appropriate databases—some services might need SQL, others NoSQL
- Establish company-wide guidelines for coding standards, testing, and documentation
Pro Tip: Don't go overboard with variety—use flexibility where it counts, but keep things maintainable.
Step 4: Containerize Microservices with Docker
Packaging each microservice into a container ensures it’s portable, scalable, and isolated from other services.

Key Actions:
- Build Docker images for each microservice.
- Ensure all dependencies are packaged within the container
- Test locally and in staging environments for consistent behavior
Pro Tip: Use multi-stage builds to keep Docker images lightweight and secure.
Step 5: Orchestrate with Kubernetes or Similar Tools
As your number of microservices grows, manual deployment becomes infeasible. That’s where orchestration tools like Kubernetes step in.

Key Actions:
- Deploy containers using Kubernetes (or alternatives like AWS ECS, Docker Swarm)
- Set up service discovery and load balancing between containers
- Use Helm charts for repeatable deployments
Pro Tip: Leverage Kubernetes’ auto-scaling capabilities to handle eCommerce traffic spikes.
Step 6: Implement API Gateway and Service Communication
Microservices need to talk to each other securely and efficiently. An API Gateway serves as the single entry point to manage these interactions.

Key Actions:
- Use API gateways like Kong, AWS API Gateway, or NGINX
- Handle routing, rate limiting, authentication, and request transformation through the gateway
- Choose appropriate protocols (REST, gRPC) and message brokers (Kafka, RabbitMQ) for service-to-service communication
Pro Tip: Keep internal and external APIs separate to improve security and control.
Step 7: Set Up Centralized Monitoring and Logging
With many services running independently, observability becomes critical for performance and debugging.

Key Actions:
- Integrate monitoring tools like Prometheus, Grafana, and New Relic
- Set up logging with the ELK Stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana) or Fluentd
- Track metrics like uptime, response times, and error rates for each microservice
Pro Tip: Use correlation IDs to trace a user request across multiple services.
Step 8: Automate with CI/CD Pipelines
To support the rapid development and deployment of microservices, automation is essential.

Key Actions:
- Build CI/CD pipelines using Jenkins, GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, or Bitbucket Pipelines
- Automate testing (unit, integration, contract) and deployments to staging/production
- Enable automated rollbacks in case of failure
Pro Tip: Use feature flags for safe rollouts and A/B testing.
Step 9: Implement Robust Security Measures
Security must be embedded from the beginning—not bolted on afterward.

Key Actions:
- Secure APIs using OAuth 2.0, JWTs, and HTTPS
- Isolate services using network policies and firewalls
- Regularly scan containers and code for vulnerabilities
Pro Tip: Make security part of your CI/CD pipeline using automated tools like Snyk or Aqua Security.
Step 10: Continuously Iterate and Optimize
Microservices are not a one-and-done project. They require ongoing iteration, refactoring, and performance tuning.

Key Actions:
- Schedule regular code reviews and architectural assessments
- Decommission or refactor underperforming services
- Gather user feedback to guide enhancements
Pro Tip: Implement a service registry (like Consul or Eureka) for dynamic service discovery and lifecycle management.
By following these steps, you can transition from a tightly coupled monolith to a flexible, scalable, and high-performing microservices architecture that grows with your eCommerce business. The key is to start small, automate early, monitor deeply, and iterate continuously.
Managing Microservices Over Time
Successfully implementing microservices is just the beginning—the real challenge lies in managing them effectively over the long term. As your microservice ecosystem grows, maintaining stability, performance, and agility requires ongoing effort, solid governance, and the right tooling.
Here's how to stay in control and continue delivering value without letting complexity spiral out of control:
1. Service Lifecycle Management
Each microservice has its own lifecycle—from development and deployment to maintenance, versioning, and eventual deprecation. Without a plan, you risk accumulating “service sprawl.”

Best Practices:
- Document ownership: Assign clear ownership for each service to specific teams
- Version control: Use semantic versioning to manage backward compatibility and rolling upgrades
- Retirement protocols: Regularly audit services and decommission those that are outdated or unused
Tip: Keep a service catalog or registry (e.g., Backstage, Consul) to track status, endpoints, and ownership.
2. Monitoring, Logging & Observability
In a distributed system, traditional monitoring falls short. You need comprehensive observability to identify bottlenecks, debug errors, and understand system behavior in real time.

Key Tools:
- Monitoring: Prometheus, Grafana, Datadog, New Relic
- Logging: ELK Stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana), Fluentd
- Tracing: OpenTelemetry, Jaeger, Zipkin
Best Practices:
- Collect logs, metrics, and traces from every service
- Implement centralized dashboards for visibility
- Set automated alerts for latency, errors, and resource limits
Tip: Use correlation IDs to trace user sessions across multiple microservices.
3. Security Maintenance
With more entry points and data flows, security becomes more complex in a microservices environment. Ongoing management is critical to prevent vulnerabilities from slipping through the cracks.

Key Actions:
- Enforce mutual TLS for service-to-service communication
- Use OAuth 2.0 or JWT for authentication
- Regularly scan containers and dependencies for vulnerabilities with tools like Snyk or Aqua
- Apply least privilege access control via role-based access (RBAC) and network policies
Tip: Automate security updates in your CI/CD pipelines to reduce manual patching.
4. Configuration & Secrets Management
Each microservice has its own configuration—often per environment. Poor configuration handling can lead to instability and data breaches.

Best Practices:
- Use centralized configuration tools like Spring Cloud Config or HashiCorp Consul
- Store sensitive data (API keys, DB passwords) in secret management tools like Vault, AWS Secrets Manager, or Kubernetes Secrets
- Automate configuration changes through GitOps workflows
Tip: Avoid hardcoding configs or secrets—this is a common and dangerous anti-pattern.
5. Automated Deployments and Rollbacks
As the number of microservices increases, manual deployment becomes a bottleneck. You need reliable, repeatable deployment practices across services.

Best Practices:
- Use CI/CD tools (e.g., GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, Jenkins) to automate builds, tests, and deployments
- Integrate canary or blue/green deployments for safe rollouts
- Implement automated rollback strategies triggered by error thresholds or failed health checks
Tip: Use feature flags to release new functionality gradually and safely.
6. Testing Across Services
Testing in microservices requires more than just unit tests. You need to ensure that individual services and their interactions work as expected.

Testing Strategies:
- Unit testing for isolated service logic
- Contract testing to verify API agreements (e.g., Pact)
- Integration testing across service boundaries
- End-to-end testing for real-world scenarios
Tip: Automate tests within your CI/CD pipeline to catch issues early.
7. Service Coordination and Communication
As more services come online, managing how they talk to each other becomes critical for performance and reliability.

Best Practices:
- Avoid tight coupling—use event-driven architectures where possible
- Use asynchronous messaging with Kafka, RabbitMQ, or AWS SQS to reduce latency and failures
- Implement circuit breakers and retry logic to handle network issues gracefully
Tip: A service mesh like Istio can provide observability, security, and traffic control for inter-service communication.
8. Team Structure & Organizational Alignment
Managing microservices at scale requires alignment across people, process, and technology.

Organizational Tips:
- Use the “you build it, you run it” approach—developers maintain ownership post-deployment
- Structure teams around business capabilities, not technical layers
- Promote cross-functional collaboration between developers, DevOps, QA, and security
Tip: Consider adopting a DevOps or SRE model to sustain long-term microservices reliability.
Managing microservices over time is about staying proactive, not reactive. With the right architecture, automation, monitoring, and team culture, you can keep your eCommerce platform robust, agile, and customer-ready—no matter how complex it gets.
How Lizard Global Helps You Succeed with Microservices
At Lizard Global, we specialize in architecting and scaling powerful eCommerce platforms using modern microservices infrastructure. Whether you're transitioning from a legacy monolith or launching a high-performance platform from scratch, we help you:
- Design and implement microservices with optimal service boundaries
- Integrate CI/CD pipelines for seamless development and deployment
- Build resilient systems with smart monitoring and alerting tools
- Secure your services with best-in-class practices and API management
- Scale your infrastructure using Kubernetes and cloud-native tools
Our team of experts ensures your digital commerce business is fast, flexible, and future-ready, empowering you to stay ahead in a competitive marketplace.
Ready to revolutionize your eCommerce architecture with microservices? Let’s connect and make it happen.
Join 2000+ subscribers
Stay in the loop with everything you need to know
FAQs

How do microservices differ from monolithic architecture?
When should I use microservices?
Are microservices only for large businesses?
What technologies are used in microservices architecture?
What is a service mesh in microservices?
How is data managed in a microservices setup?
How do you test microservices?
Are microservices secure?
Can microservices be hosted on the cloud?
similar reads







